Creating a branch
Create a branch to start an independent line of policy development. You can create a branch at the root level, import a snapshot as a new branch, or base a subbranch on a commit in an existing branch.
Creating a root branch
Create a root branch to begin a new line of policy development from scratch.
|
You can create up to 100 root branches in the Policy Editor, including system and self-governance branches that might not be visible to the user. The Branch Manager displays a visual counter showing how many branches have been created out of the 100-branch limit. |
Steps
-
In the Policy Editor, go to Branch Manager > Version Control.
-
From the menu, select Create new root branch.
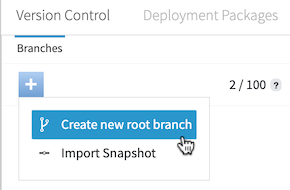
-
Enter a name for the new branch.
Branch names must be unique.
-
Click Save Branch.
Importing a snapshot
Import previously exported snapshot files as branches to share and restore Trust Framework definitions and policies across users and environments.
A snapshot file contains all the entities and policies from an existing branch. Learn more in Creating a snapshot.
Steps
-
In the Policy Editor, click Branch Manager.
-
On the Version Control tab, click , and then select Import Snapshot.
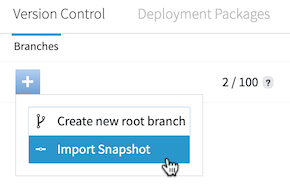
-
Select the appropriate snapshot file.
-
Specify a unique name for the branch.
-
Click Import.
-
(Optional) Click Commit New Changes to commit the initial state of the policy branch.
Creating a subbranch from a commit
You can create a subbranch as a child of a commit in another branch. The subbranch shares the history and contents of the parent branch up to that commit.
Learn more about branch commits in Committing changes.
Steps
-
In the Policy Editor, click Branch Manager.
-
On the Version Control tab, select the commit from which to branch.
To branch from the latest uncommitted changes, make sure to commit before proceeding.
-
Click the hamburger menu and select Create new branch from commit.
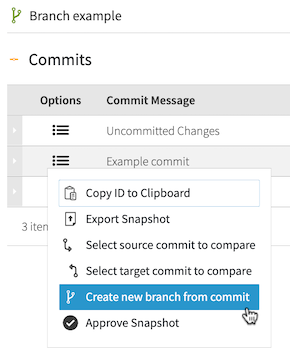
-
Specify a unique name for the branch.
-
Click Save Branch.
Result
The system creates a new subbranch with the selected commit as the branch point.