Configure server certificates
PingOne Advanced Identity Cloud protects all inbound network traffic using TLS encryption. By default, each of your tenant environments is provisioned with Google-managed certificates. If you add one or more custom domains to your tenant environments, you can optionally provide your own self-managed certificates.
Advanced Identity Cloud also lets you add certificates to each tenant environment’s truststore to protect outbound connections to your company’s other network resources.
Inbound connections
Ping Identity domains
Advanced Identity Cloud uses Google-managed certificates to secure inbound traffic to the forgeblocks.com
and forgerock.io domains used by your tenant environments.
Custom domains
Google-managed certificates (default)
If you use a custom domain to access Advanced Identity Cloud, by default a Google-managed certificate is used to secure inbound traffic to the domain. The domain is added to the certificate’s Subject Alternative Name (SAN) field.
Self-managed certificates
Advanced Identity Cloud offers you the choice of using a self-managed certificate with your custom domain, in place of the default Google-managed certificate.
You can create self-managed certificates in two main ways:
-
Use a tenant-generated private key that is only accessible by the tenant itself. The tenant generates the CSR, and you install the resulting certificate on the same tenant. Learn more in:
-
Use a locally generated private key that you retain access to. You generate the CSR locally and install the resulting certificate on as many tenants as you need. Learn more in:
DV and EV certificates
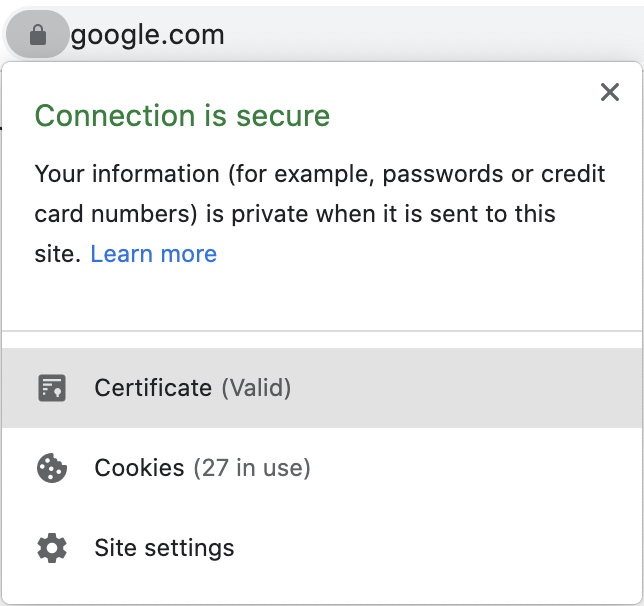
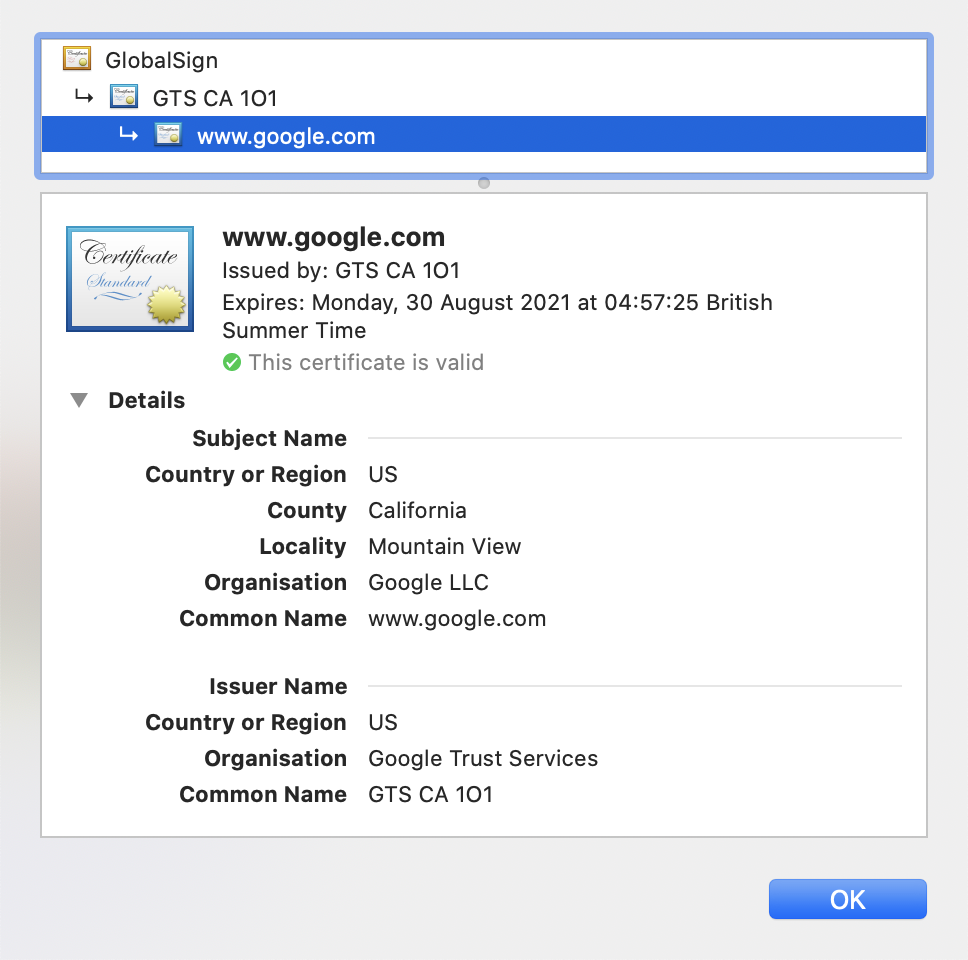
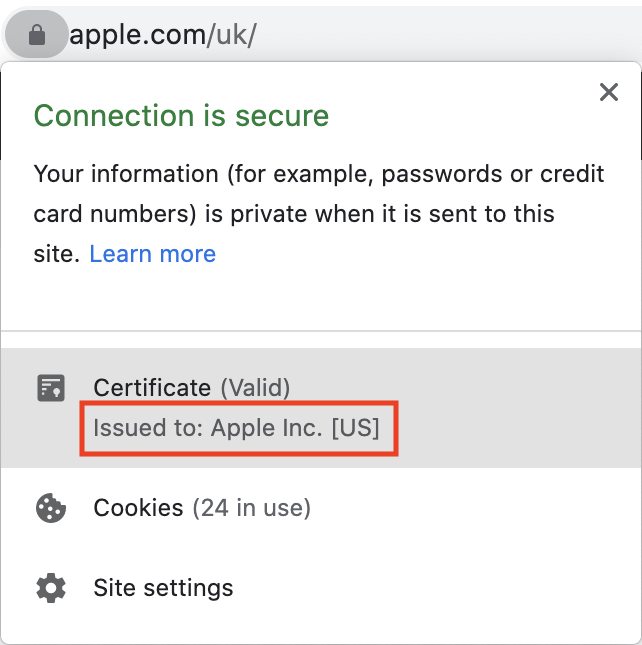
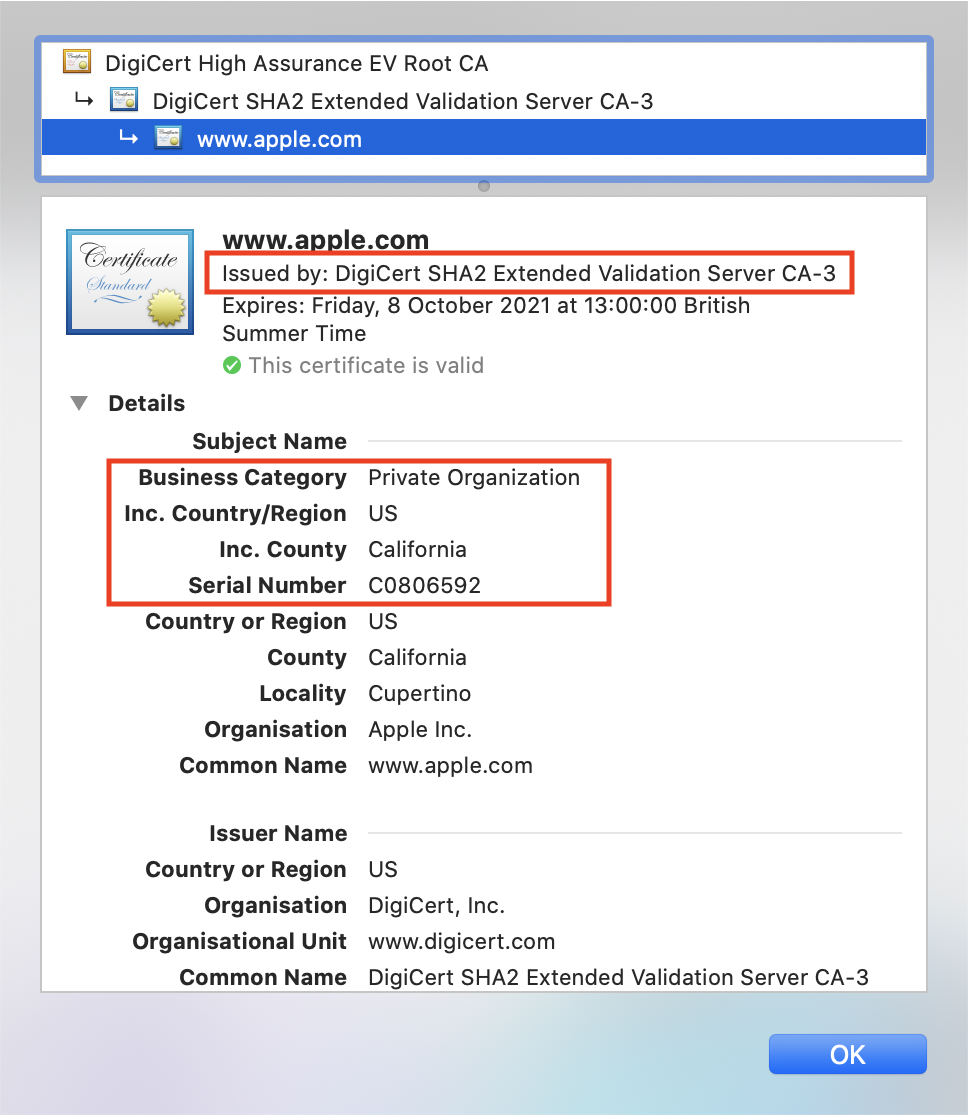
Providing your own Domain Validation (DV) or Extended Validation (EV) SSL certificate can give your end users extra confidence that your applications are secure. Most browser vendors have now removed the visual signals in the browser address bar that distinguished these certificates (green padlock, highlighted company name, highlighted https protocol). However, the additional EV certificate information is still available when you click the padlock in the browser address bar and inspect the certificate:
Standard SSL certificate: |
EV SSL certificate: |
|
|
Wildcard certificates
Wildcard certificates allow subdomains of the same domain to share a certificate in the following ways:
-
Within the same realm
-
Across different realms
-
Within the same realm and across different realms
For example, a certificate for the wildcard domain "*.example.com" could be shared between an Alpha realm using the subdomain "customers.example.com" and a Bravo realm using the subdomain "employees.example.com".
Similarly, the same certificate could be shared between subdomains "employees-emea.example.com" and "employees-apac.example.com" within the same Alpha or Bravo realm.
Outbound connections
Advanced Identity Cloud lets you secure outbound traffic from your tenant environments to your own network. For example, you might want to secure outbound emails from your Advanced Identity Cloud tenant environments to your on-premises SMTP server.
To do this, supply your own CA or TLS certificates to Ping Identity. Ping Identity then adds the certificates into the trust store of your tenant environments. You can supply as many certificates as you need.
Send Ping Identity a CA or TLS certificate
-
Click Create a case.
-
Follow the steps in the case submission wizard by selecting your account and contract and answering questions about your tenant environments.
-
On the Please answer the following questions to help us understand the issue you’re facing page, enter the following details, and then click Next:
Field Value What product family is experiencing the issue?
Select PingOne Advanced Identity Cloud
What specific product is experiencing the issue?
Select Configuration
What version of the product are you using?
Select NA
-
On the Tell us about the issue page, enter the following details, and then click Next:
Field Value Provide a descriptive title for your issue
Enter
Add CA or TLS certificate to tenant trust storesDescribe the issue below
Enter a comma-separated list of FQDNs for your sandbox[1], development, UAT[2], staging, and production tenant environments.
-
Click Submit.
-
Upload the local file containing your certificate.
-
Ping Identity support confirms when the certificate has been imported into the trust stores of your tenant environments.